Beverages

Key Points
- Stevia is a natural choice for sweetening a wide variety of beverages such as teas, coffees, soft drinks, flavored waters, juices and alcoholic beverages
- Stevia solutions formulated for specific beverage applications can provide a superior, clean, sugar-like taste with reduced linger
- Stevia is stable in most beverages throughout processing and storage
Stevia is a natural choice utilized by leading beverage brands in a variety of strategic approaches to market such as innovation, artificial sweetener replacement, sugar moderation for kids and cost savings. Stevia’s geographic and category penetration have grown rapidly over the past several years. Between 2012 and 2017 alone, more than 1500 global new beverage product launches were made with stevia encompassing ready-to-drink (RTD) teas, sweetened coffee beverages, carbonated soft drinks (CSDs), flavored waters, juices and alcoholic beverages.
Functionality and Stability in Beverage Applications
Stevia’s rapid growth in the beverage market is a testament to its many benefits including: zero calories, 100% natural origin, non-caloric, tooth-friendly, pH stable, non-fermenting, highly soluble, heat stable, photo (light) stable and shelf stable. When considering shelf stability, stevia is an excellent sweetener choice for CSDs which typically have a low pH, especially in light of the wide range of temperatures CSDs experience during shelf life in some markets.
Research confirms the notable stability properties of stevia. A 2008 study of lemon-lime and cola CSDs demonstrated that both rebaudioside A and stevioside are stable when exposed to sunlight.1 Another study found that in aqueous solutions stevioside is remarkably stable in a pH range of 2–10 under thermal treatment up to 80°C for over two hours. In an aqueous solution enriched with B-vitamins, no significant changes in stevioside and B-vitamin levels were seen when incubated for up to four hours at 80°C. In addition, a protective effect of stevioside on the degradation of ascorbic acid was observed resulting in a significant delayed degradation rate.2 In a seminal study published in 1983, no significant chemical, microbiological or sensory changes were found when stored at room temperature for three and five months for CSDs formulated with rebaudioside A and stevioside respectively. In addition, heating at 60°C for six days resulted in only a 0-6% loss of the sweeteners.3
In November 2011, the European Commission approved Regulation EU 1131/2011 granting authorization of the use of steviol glycosides as a sweetener in foods and beverages.4 This was following the European Food Safety Authority’s (EFSA) April 2010 positive scientific opinion on the safety of steviol glycosides.
Tips on Formulating Beverages with Stevia
Stevia not only imparts sweetness, but can also function as a flavor modifier in some instances. Depending on the beverage type, it is important to consider how stevia interacts with the overall flavor, acidity, mouthfeel and sweetness. Stevia can work well with other sweetener systems to provide taste synergies between classic products and new formulations. When used to replace some of the sugar in a formula, a significant reduction in added sugar and calories can be achieved without sacrificing taste or texture.
Some tips for optimizing the sweetness profile of stevia in beverage applications include: blending small amounts of caloric or other non-caloric sweeteners (such as sucrose, fructose and polyols), utilizing blends of acids such as citric + malic, adding sodium salts and incorporating blends of steviol glycosides. When reducing sugar, adding varying weighting agents such as gums, fiber, sugar alcohols and juice concentrates can help improve thickness perception. The types of stevia blends selected should be influenced by flavor, for instance terpene aromatics might be better complimented by blends made with rebaudioside A.
Formulating beverages with stevia presents some unique challenges such as a high sweetness max, sweetness linger and a strong aftertaste. Therefore, to enable optimal taste with stevia, PureCircle’s® innovative family of stevia products called Sigma-Beverage consist of proprietary combinations of steviol glycosides that provide a superior, clean, sugar-like taste with a reduced linger and have been especially researched and developed for a variety of beverage applications.5
Carbonated Soft Drinks
The CSD category continues to be a leading product category for the launch of new stevia products around the world. In 2015 there were 86 new cola flavored CSDs and 25 new lemon-lime flavored CSDs formulated with stevia. Each type of CSD such as cola, orange or lemon-lime has a unique flavor and acid profile which benefits from the right combination of steviol glycosides to provide the cleanest sweetness. A sensory panel conducted at PureCircle® compared a zero-calorie cola flavored CSD made with two different blends of Rebaudioside A ingredients, Reb-A 97 and Reb-A 99 (figure 1).6 Results found that the cola made with Reb-A 99 was significantly lower in bitterness and spice intensity.
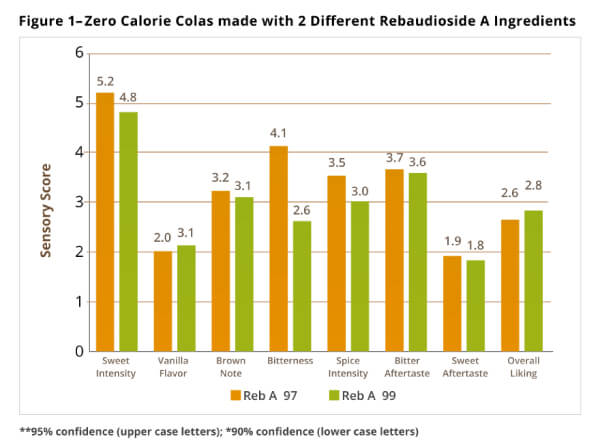
The major ingredient in CSDs is sugar, typically sucrose or high fructose corn syrup. Sweetening very low to zero calorie CSDs solely with stevia can be especially challenging and often-times stevia is blended with sugar and other sweeteners to achieve a more sugar-like taste. Recent research shows that specific combinations of steviol glycosides taste better than single steviol glycosides like Reb A or Reb D in a variety of food and beverage categories for deeper sugar reductions with a cleaner taste profile.
Tea and Coffee
Tea is a prized drink around the world and has been for centuries. It has transcended different cultures to become one of the largest beverage categories today. Whether consumed hot or cold, sweetening tea is a must for many consumers. Options to sweeten tea beverages, either at home or in RTD form, are vast from sugar to fruit extracts to artificial sweeteners and most recently with stevia: in 2015 alone, there were 392 new RTD teas sweetened with stevia.
Sigma-T from PureCircle® is a proprietary combination of steviol glycosides researched and developed specifically for the RTD tea category. It can provide a clean sweetness profile with reduced astringency, bitterness and sweet aftertaste while complementing the herbal, earthy notes found in most teas. In a sensory study of a 50% reduced sugar iced lemon black tea, Sigma-T performed at parity to sugar and showed improvement in astringency and bitter aftertaste (figure 2)6.
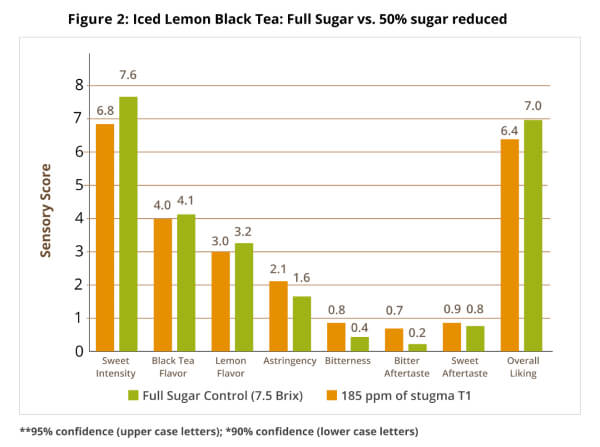
Coffee is a beloved drink all around the world and in many cultures, it has been a part of the human lifestyle for centuries. Over the past five years, iced coffee has become a strong growing segment in the coffee category.7 Today’s consumers are not only buying iced coffee at local coffee shops, but they also want the convenience of having cold brewed coffee at home. Beverage companies have been responding by delivering iced coffee, usually sweetened, right to grocery store shelves.
As this trend continues, formulators are looking for options to provide this sweet drink to consumers without extra calories. Stevia based sweeteners can help create delicious iced coffee formulations with low-to-no calories from added sugars while enhancing rich roasted coffee notes. It also can enhance the mouthfeel perception in iced coffee to make it seem creamier.
Research confirms the benefits of sweetening coffee and tea beverages with stevia. In a study to determine the ideal sweetness level in beverages prepared with instant ground coffee and roasted coffee, a formulation with 0.095% stevia leaf extract was equivalent in ideal sweetness to that of 9.5% sucrose.8 Research on espresso coffee indicates that a formulation with 0.0998% stevia leaf extract was similar in ideal sweetness profile to that of 12.5% sucrose.9
Juice
Consumers are looking for less sugar and premium juice products, they are also demanding products that provide value-added benefits. According to Euromonitor International, juice volume sales in the United States continued to decline in 2016 as consumers turned away from juices due to concerns about their high sugar content.10 As demand grows to reduce overall calories and sugars from juice drinks, developers have been tasked with maintaining the sweet tastes consumers have become accustomed to. While juice drinks obtain a portion of sweetness from the natural sugars present in the juices used, added sugars are often used to enhance the sweetness profile and have subsequently added calories to diets.
Studies confirm that stevia can facilitate sugar reductions without compromising taste. A recent study on peach juice determined that a binary mixture of stevioside and sucrose yielding a 25% reduction in calories was not significantly different in acceptability compared to a full sugar control with 9% sucrose.11 As an added benefit, stevia is also stable under normal thermal as well as high pressure processing conditions.
Other Beverage Applications
As consumers work to cut calories from their diets, they are turning to flavored waters, both still and sparkling, to keep them refreshed versus traditional alternatives. In fact, flavored water launches have doubled over the last five years, according to Mintel Market Intelligence.12 In 2016 alone, over 800 flavored waters were launched globally giving consumers more choice in hydration options. Stevia has enabled developers to meet consumer demands by providing zero-calorie sweetness that compliments and enhances these beverages. Instead of adding sugar or a non-natural option, developers can now turn to stevia to offer flavorful sweetness without the extra calories.
Stevia can also be utilized to reduce sugar in alcoholic beverages such as beer and cocktails. Research on a reduced calorie lemon flavored beer indicates that replacing the sucrose with 25% stevia, 50% isomalt and 25% sucrose had no negative effect on the qualitative traits and taste of the beer.13 When using stevia in alcohol applications, it is important to consider the alcohol content (%abv), alcohol source and flavor. In general, alcohol decreases sweetness perception so one has to start with a sweetness target about 10% higher than for a non-alcoholic beverage. In drinks containing more than 9% alcohol, it is recommended to use a blend of steviol glycosides.
Stevia is a powerful ingredient to reduce and/or eliminate sugars from a variety of beverage applications. Its many benefits include; zero calories, natural origin, superb functionality, stability and flexible of use in a wide variety of beverage categories such as CSDs, coffees, teas, juices, flavored waters and alcoholic beverages. Category-specific stevia solutions allow deeper sugar reductions while preserving true flavor and superior mouthfeel.
REFERENCES
- Clos J, et. al. Photostability of rebaudioside A and stevioside in beverages. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:8507-13.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jf801343e
- Kroyer G. Stevioside and Stevia-sweetener in food: application, stability and interaction with food ingredients. J Verbrauch Lebensm, 2010;5:225-9.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00003-010-0557-3
- Chang S and Cook J. Stability studies of stevioside and rebaudioside A in carbonated beverages. J Agric Food Chem. 1983;31:409-12.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf00116a056
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 1131/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to steviol glycosides. 2011;12: 205–6. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32011R1131
- Food Business News. PureCircle launches Sigma-Beverage [published 2016 Nov 22] Sosland Publishing. Web [accessed 2017 Aug 10] Available at:https://www.foodbusinessnews.net/articles/7225-purecircle-launches-sigma-beverage
- PureCircle. Stevia and The PureCircle Advantage. 2016.
- Sisel E. The Strength of Cold Brew. [published 2016 Jul 29] Mintel Blog. [accessed 2017 Aug 10] Available at:http://www.mintel.com/blog/drink-market-news/the-strength-of-cold-brew
- Moraes T, et al. Different sweeteners in beverages prepared with instant and roasted ground coffee: Ideal and equivalent sweetness. J Sens Stud, 2010;25:215-25.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-459X.2010.00275.x
- Azevedo B, et. al. High‐intensity sweeteners in espresso coffee: ideal and equivalent sweetness and time–intensity analysis. Int J Food Sci Tech. 2015;50:1374-81.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/ijfs.12774
- Beverage Industry. 2017 State of the Industry: No added sugar, fortification in demand for juice, juice drinks [published 2017 Jul 12] BNP Media. Web [accessed 2017 Aug 11] Available at:http://www.bevindustry.com/articles/90349-state-of-the-industry-no-added-sugar-fortification-in-demand-for-juice-juice-drinks
- Parpinello G, et. al. Stevioside as a replacement of sucrose in peach juice: sensory evaluation. J Sens Stud., 2001;16:471-84. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1745-459X.2001.tb00314.x
- Mintel. Water Market – Global Annual Review – 2016. Available at:https://store.mintel.com/water-market-global-review-2016
- 13. Ranji R, et. al. Stability of lemon beer containing stevia and isomalt sweeteners during storage period. [BEPLS Bulletin] Env Pharmacol Life Sci. 2014;3(III):145–50. http://www.bepls.com/special_3_2014.html

